Refrigerants used in Fujitsu units
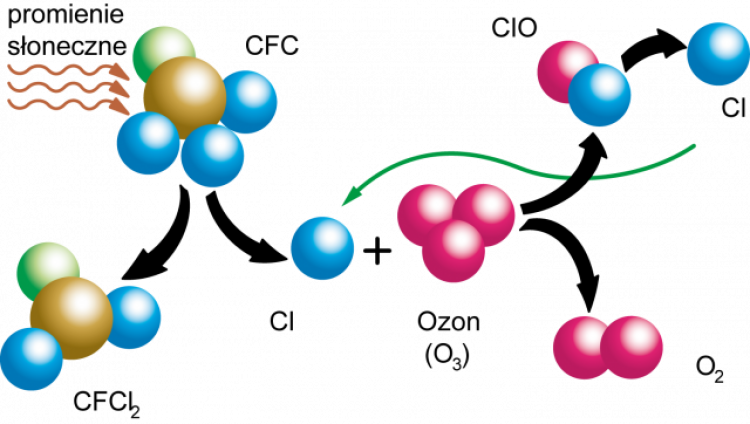
The reasons for which chlorine-containing agents are being phased out result from the discovery of certain phenomena occurring after such agents have been released to the atmosphere. When released from the installation, a molecule of an ozone depleting substance travels as far as the stratosphere (15 ÷ 50 km above the earth). Under the influence of UV radiation, the process of photodissociation takes place, where a chlorine atom separates from the refrigerant molecule, and breaks the ozone molecule. This reaction creates: chlorine oxide + oxygen molecule (Cl+O3=ClO+O2) is formed, then chlorine oxide reacts with another ozone molecule (ClO+O3=Cl+2O2), etc. It is estimated that a single chlorine atom can destroy 10 ÷ 100,000 ozone particles.
The Fujitsu devices which are currently being launched on the market use: R407C and R410A refrigerants whose ozone depletion factor equals 0 (they do not contain chlorine atoms).
The basic differences are briefly described in the table below:
|
|
HCFC REFRIGERANTS
|
HFC REFRIGERANTS
(do not contain chlorine atoms)
|
|
|
NAME OF REFRIGERANT
|
R22
|
R407C
|
R410A
|
|
CHEMICAL FORMULA / COMPONENTS
|
CHClF2
|
HFC32 / HFC125 / HFC134a
|
HFC32 / HFC125
|
|
MIXTURE COMPOSITION [%]
|
100
|
23 / 25 /
52
|
50 / 50
|
|
TYPE OF MIXTURE
|
SINGLE COMPONENT
|
ZEOTROPIC MIXTURE1
|
AZEOTROPIC MIXTURE2
|
|
SATURATION PRESSURE
26ËšC [MPa]
|
0,9714
|
1,126
|
1,608
|
|
OZONE DEPLETION POTENTIAL ODP
|
0,034
|
0
|
0
|
|
GLOBAL WARMING POTENTIAL GWP
|
1700
|
1700
|
2000
|
|
OIL
|
MINERAL OIL (SUNISO)
|
SYNTHETIC (ETHER OR ESTER)
|
|




 Poland
Poland Sweden
Sweden Finland
Finland German
German Estonia
Estonia